XDMA to transfer data between hosts and FPGAs
- Install the XDMA driver
- Setting up the XDMA engine
- AFI Configuration Overview
- Confirmation of setup
- Run XDMA sample code
- About host—FPGA performance
AWS FPGA HDK/SDK provides host memory, XDMA engine on FPGA Shell for data transfer between FPGA memory, and XDMA driver that runs on the host it’s
XDMA driver
- Open source
- Multichannel interface
- Perform data transfer using DMA from the application using standard POSIX APIs such as open () /read () /write ()
- Use standard POSIX APIs such as open () /poll () from your application to perform user space interrupt/event notifications
Install the XDMA driver
Follow these steps to install the XDMA driver:
$ sudo systemctl stop mpd
$ sudo yum remove -y xrt xrt-aws # Environment (XRT). Remove XOCL driver
$ cd ~/aws-fpga/sdk/linux_kernel_drivers/xdma
$ make
$ sudo make install
$ lsmod | grep xdma # Verify that the XDMA driver is installed
Setting up the XDMA engine
Here we will load the pre-prepared AFI. Clear the slot, then perform the load and finally check the status of the FPGA slot
$ sudo fpga-clear-local-image -S 0
$ sudo fpga-load-local-image -S 0 -I agfi-0b5c35827af676702
$ sudo fpga-describe-local-image -S 0 -H
For more information about the contents of AFI, please refer to the following link: https://github.com/aws/aws-fpga/tree/master/hdk/cl/examples/cl_dram_dma
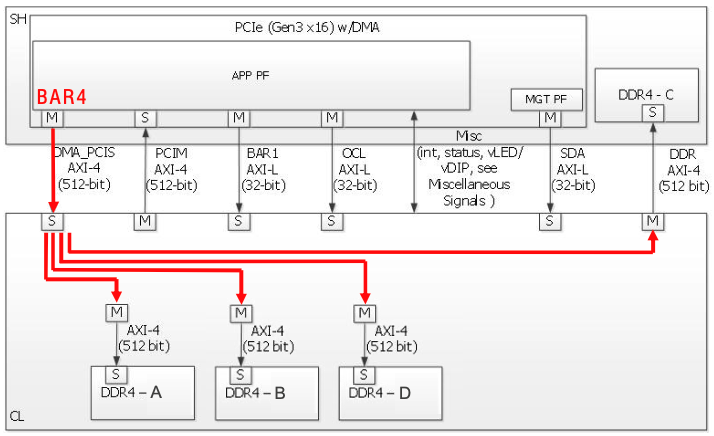
AFI Configuration Overview
In this AFI, four DRAM channels are mapped over the appPF BAR4 memory space via the DMA_PCIS interface.
DDR_A (base_addr=0x0_0000_0000, 16GB)
DDR_B (base_addr=0x4_0000_0000, 16GB)
DDR_C (base_addr=0x8_0000_0000, 16GB)
DDR_D (base_addr=0xC_0000_0000, 16GB)
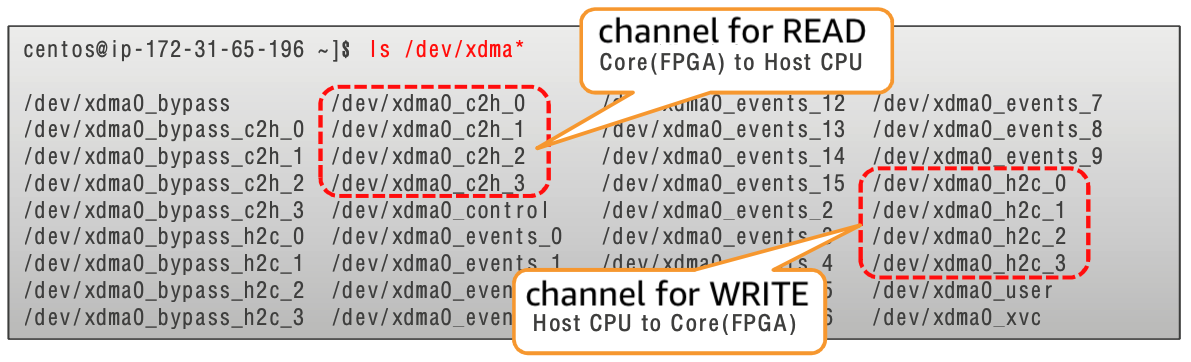
Confirmation of setup
- Once XDMA setup is complete, the available XDMA appears on /dev/ as a device file.
- You can see that there are 4 channels of READ and WRITE.
- XDMA driver also supports interrupt/event notification.
- Interrupts are reported as mSI-X interrupts to PCIe apppf.
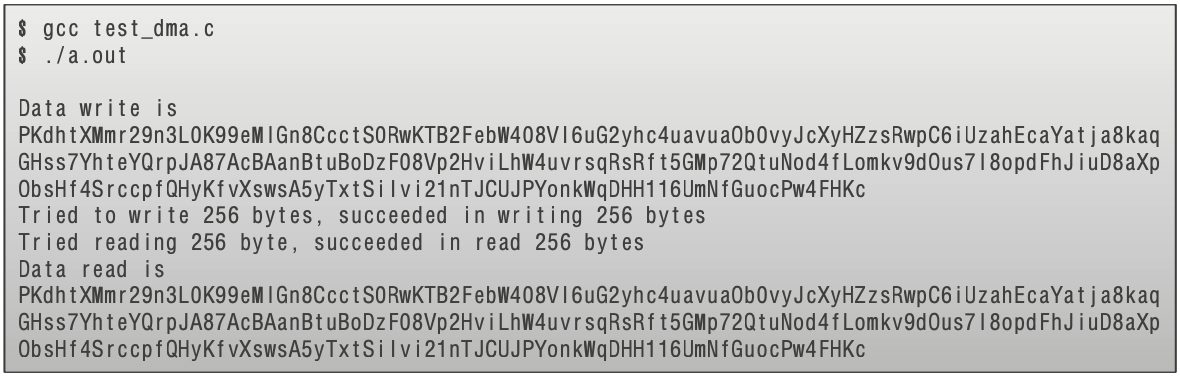
Run XDMA sample code
- Run the sample code in the link below
- Save the sample code under the file name test_dma.c and run it.
XDMA sample code
test_dma.c (host application code 1/4)
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define BUF_SIZE 256
#define OFFSET_IN_FPGA_DRAM 0x10000000
static char *rand_str (char *str, size_t size)//randomize a string of size <size> //Lunders of the specified size, Generate a mad string
{
const char charset [] = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvxyzuvxyzabcdefhijklmnopqlmnopqlmnopqrtSUVXYZ1234567890";
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++) {
int key = rand ()% (int) (sizeof charset - 1);
str [i] = charset [key];
}
str [size-1] = '\ 0';
return str;
}
test_dma.c (host application code 2/4)
- on host memory
- Secure buffer
- Show generated data, Add to linked code
- Host Memory → Open DMA Channel for WRITE to FPGA Memory
int main () {
char* srcBuF;
char* dstBuf;
int read_fd;
int write_fd;
int i;
int ret;
on host memory
Secure buffer
srcBUF = (char*) malloc (buf_size* sizeof (char)); // on host memory
// Secure buffer
dstBuf = (char*) malloc (buf_size* sizeof (char));
/* Initialize srcBuF */
rand_str (srcBUF, BUF_SIZE);
printf ("Data write is%s\ n", srcBuF); // Show generated data*Add to linked code
/* Open a XDMA write channel (Host to Core) */
if ((write_fd = open ("/dev/xdma0_h2c_0", O_WRONLY)) == -1) { // Host Memory → Open DMA Channel for WRITE to FPGA Memory
perror ("open failed with errno");
}
test_dma.c (host application code 3/4)
- Open DMA channel for READ from FPGA memory to host memory
- Transfers random string data prepared on host memory to FPGA memory
- Data written to FPGA memory is transferred to host memory
/* Open a XDMA read channel (Core to Host) */
if (read_fd = open ("/dev/xdma0_c2h_0", O_RDONLY)) == -1) { // Open DMA channel for READ from FPGA memory to host memory
perror ("open failed with errno");
}
/* Write the ENTIRE source buffer to offset OFFSET_IN_FPGA_DRAM */
ret = pwrite (write_fd, srcBUF, BUF_SIZE, OFFSET_IN_FPGA_DRAM); // Transfers random string data prepared on host memory to FPGA memory
if (ret < 0) {
perror ("write failed with errno");
}
printf ("Tried to write %u bytes, succeeded in writing%u bytes\n", BUF_SIZE, ret);
ret = read (read_fd, dstBUF, BUF_SIZE, OFFSET_IN_FPGA_DRAM); // Data written to FPGA memory is transferred to host memory
if (ret < 0) {
perror ("read failed with errn");
}
printf ("Tried reading%u byte, succeeded in read%u bytes\ n", BUF_SIZE, ret);
test_dma.c (host application code 4/4)
- Displays data transferred from FPGA memory to host memory
if (close (write_fd) < 0) {
perror ("write_fd close failed with errno");
}
if (close (read_fd) < 0) {
perror ("read_fd close failed with errno");
}
printf ("Data read is%s\ n", dstBuF); // Displays data transferred from FPGA memory to host memory
return 0;
About host—FPGA performance
-
Host and FPGA connected via PCIe x16, Gen3
- Due to PCIe specifications, effective transfer rates at the data link layer are 15.75Gb/sec one-way, bi-directional Direction 31.5Gb/sec
-
XDMA performance
- HDK/SDK provides XDMA engine on shell and XDMA runtime driver that runs on the host
- READ 12.8Gb/s, WRITE 11.5Gb/s
- FIO Benchmarking Techniques for DMA